You’ve probably heard the term “serverless computing in cloud” and wondered: “How can there be no servers?”
Here’s the truth: there are still servers — you just don’t have to manage them.
This is what makes serverless computing a game-changer. It lets developers focus on writing code while the provider of cloud hosting handles everything like scaling, infrastructure, and uptime. In this blog, we’ll break down what serverless computing is in the cloud, how it works, and why it’s becoming so popular.
Let’s dive in.
What Does The Term Serverless Mean In Cloud Computing?
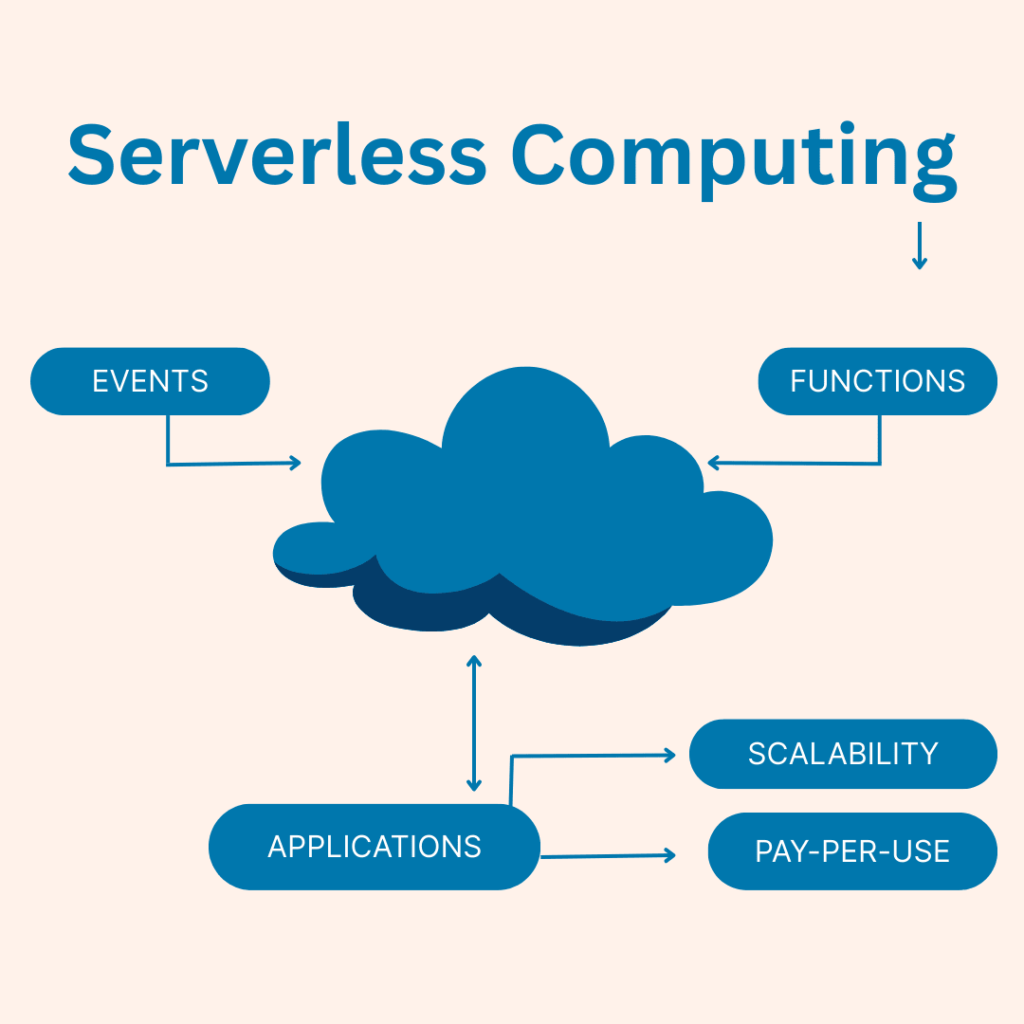
Despite its name, serverless computing still uses servers — you don’t have to worry about managing them as a developer or business.
Simply, serverless computing allows you to execute code without provisioning or managing servers. You write and deploy your application or website, and the cloud provider handles everything behind the scenes, such as scaling, infrastructure, and uptime.
The best part? You are only required to pay for the resources that were actually used. For example, you will only be billed for the resources that were consumed while you were executing a code. This makes serverless computing in cloud ideal for event-driven apps, such as handling a file upload, delivering a notification, or driving an API.
Key Characteristics of Serverless Computing in the Cloud:
- No Server Management: There will be no need for you to suffer the technical headache of managing or updating the server, operating system, and the infrastructure.
- Pay-per-use: You are charged only for the resources that were consumed by your codes, which is very cost-effective.
- Automatic Scaling: The cloud provider will automatically adjust the scale of resources as per your demand
- Typically event-driven: serverless functions permit the adoption of reactive and event-driven architectures.
- Code focus: You can now concentrate on code writing and deployment, all the while speeding up the development cycle immensely.
Read More: Why would you need a dedicated server for accounting firms.
So What Exactly Happens in Serverless Computing in cloud?
Here’s how serverless cloud computing works in simple terms:
- You write a small piece of code (called a function ) that does something specific, like sending an email, resizing an image, or processing a payment.
- This method is called by an event, such as a user clicking a button, uploading a file, or submitting a form.
- Your function is hosted by the cloud provider on its own infrastructure, automatically allocated the resources it needs, and turned off when it’s finished.
- And the best part? You only pay for the time your function is actually running.
No servers. No idle costs. Just code that runs when needed.
Benefits of Serverless Computing
Here’s why people should choose invisible computing:
- Reduced Cost: Pay-as-use pricing models greatly reduce the amount of expenditure when used for an application or website with variable workloads or occasionally accessed features.
- Agility and Convenience: You can focus on the core of your business logic and ensure faster development cycles to promote the productivity and efficiency of your business.
- Improved Scalability: Auto-scaling helps ensure that your application or website scales with sudden bursts in traffic to maintain performance and minimize downtime.
- Reduced Operational Overhead: Eliminating server management minimizes operational overheads and enables the free deployment of IT resources to other essential activities.
- Enhanced Reliability: Providers ensure high availability and fault tolerance, with minimized downtime, leading to enhanced reliability of the website or application.
Common Use Cases (When Should You Use Serverless?)
Not every app is a good fit, but here are some great scenarios where serverless computing in cloud should be used:
- The APIs Backends : The building of scalable and economical APIs for applications and websites
- Data Processing: This involves handling real-time data streams, for example, from an IoT sensor and transforming data.
- Microservices: Building microservices-based architecture for better modularity, scalability, and maintainability.
- Event-driven : Handling events from disparate sources, for example, from message queues, databases, or IoT devices.
- Batch Processing: Running batch jobs such as data migration and scheduled tasks cost-effectively.
What Are the Downsides?
Like any tech, serverless computing in cloud isn’t perfect for everything. Mentioned below are the major downsides of this method.
- Cold Starts: Sometimes, if a function hasn’t been used recently, it might take some time to wake up.
- Time Limits: Most providers limit how long a single function can run (usually around 5–15 minutes).
- Vendor Lock-In: Moving between cloud platforms can be tricky because each has its own tools and setup.
- Debugging Can Be Tricky: Since you don’t control the environment, tracking down bugs can be harder.
Read More: Cloud Disaster Recovery in 2025: Your Best Defense Against Downtime!
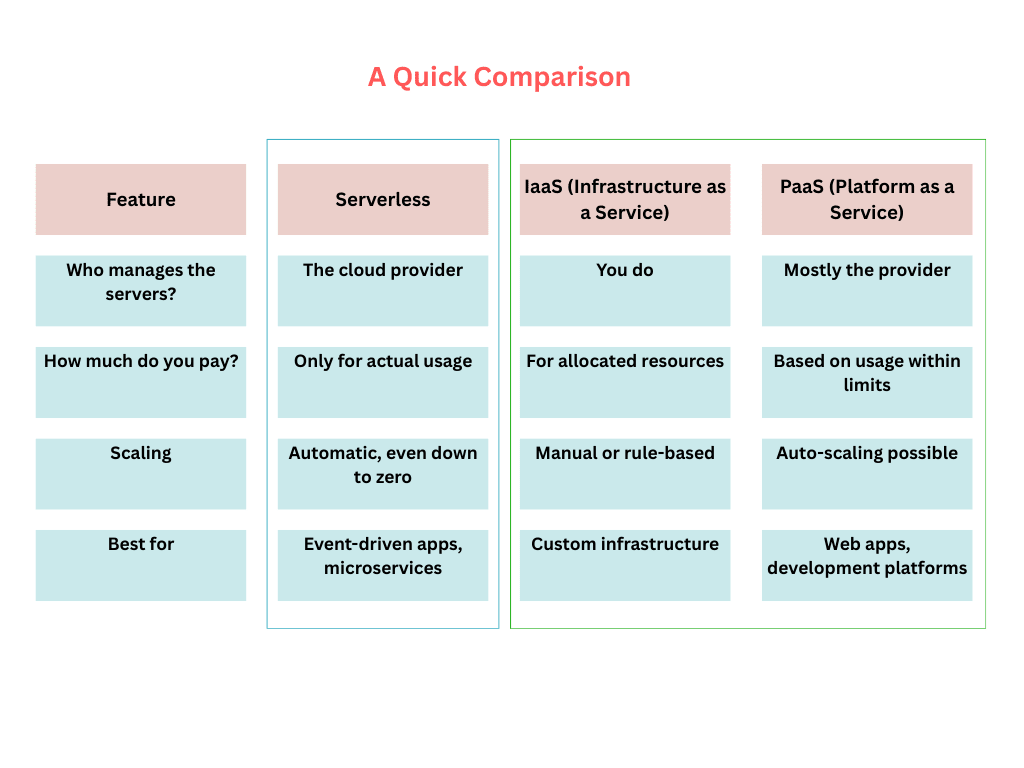
Serverless vs Other Cloud Models – A Quick Comparison
Why Developers Love Serverless Hosting?
For developers, serverless means:
- Less time spent on DevOps tasks
- Faster deployment cycles
- More freedom to build and test ideas quickly
And for businesses?
- Lower operational costs
- Easier maintenance
- Faster time-to-market
As cloud technology evolves, serverless is becoming a go-to choice for companies looking to move fast and stay lean.
Conclusion
With the shift in cloud computing, where applications and websites are created and deployed more nimbly, serverless computing in cloud is that change. Through the abstraction away from infrastructure management, it allows you to focus on the core of your business to for better innovations and streamlining operations.
It doesn’t mean everything can be achieved through serverless computing, but in cost-effective, scalable, and agile ways, it shows great advantages. For affordable cloud hosting solutions you can contact us at +1(800) 217-0394.
FAQs
Is serverless computing completely free?
No. You are always charged for whatever execution time consumed by the code, along with what data was used and associated transfers. You could also have, for example, function invocation quantities or memory usage for network traffic contributions to your price.
What is the difference between serverless computing and cloud computing?
In traditional cloud computing, you rent virtual machines or physical servers and are then responsible for operating systems, installed software, and the underlying infrastructure.. Serverless computing abstracts away all those concerns. It’s just you writing and deploying your code.
What are the limitations of serverless computing?
The key limitations of serverless computing are vendor lock-in, cold starts, concurrency limits, debugging issues, and reduced control on the infrastructure.
Can I use serverless computing for all my applications?
Serverless computing can be applied to most applications but is not necessarily a one size fits all solution. Here are the factors to consider:
a) Characteristics of the application.
b) Latency requirements.
c) Resource requirements.
d) Integration needs.
How do I get started with serverless computing in cloud?
To get started, you will need to find a cloud provider whose services fit your needs. Then, you can start with a simple project to get the gist.

Brown Lopez is a Cloud Engineer and technical writer based in Austin, USA, who enjoys turning complex cloud ideas into clear, simple insights. With solid experience in cloud architecture and real-world projects, he loves creating practical content that helps professionals understand, build, and improve their cloud solutions with confidence.