Virtual Desktop Infrastructure is a revolutionary technology that breaks up the linkage of a user’s computing experience with the hardware involved. With centrally located servers accessed at a remote location afterward over network connections, an entire virtual desktop environment, its operating systems, applications, and data, are being centrally hosted. This type of centralized hosting is a key characteristic of a virtualized desktop environment, where users can access their desktops from anywhere.
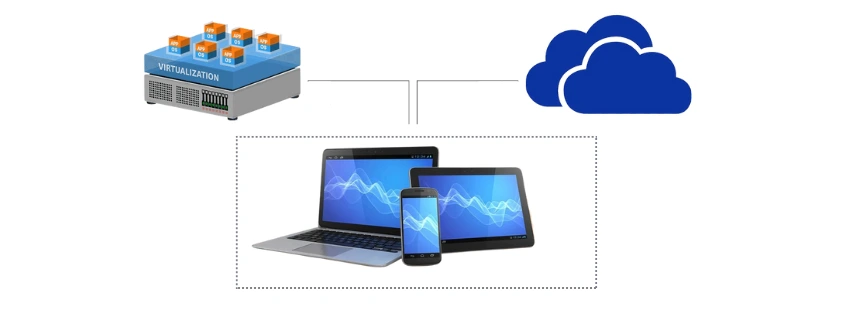
What is the VDI?
VDI is one of the virtualization technologies that gives all access and enjoyment remotely, without even downloading anything or storing anything locally. Similarly, using VDI would allow the user to work just about anywhere on any device having an available network connection, whether desktop, laptop, tablet, or even smartphone.
How does Virtual Desktop Infrastructure work?
Core to VDI are technologies in the virtualization field. This powerful technique separates physical hardware (a CPU, RAM, storage) into multiple machines that can exist virtually. The virtual machines can operate independently, with their operating systems and resources, just like a computer would. VDI meaning refers to this process where the desktop experience is separated from the physical device and is delivered via a centralized server.
The following is a step-by-step explanation of how the VDI works:
- Accessing by Users: The users request access to the VDI server with either a web-based browser or a client application.
- Resource Distribution: The resources like CPU, RAM, and storage space are distributed from the VDI server to the user’s virtual desktop.
- User Interaction: The user works on the virtual desktop like on a local machine. All the inputs, that is, keyboard, and mouse clicks are sent to the VDI server for processing.
- Output Display: The processed output (graphics, video, audio) is then transmitted back to the user’s device for display.
Types of VDI Architectures:
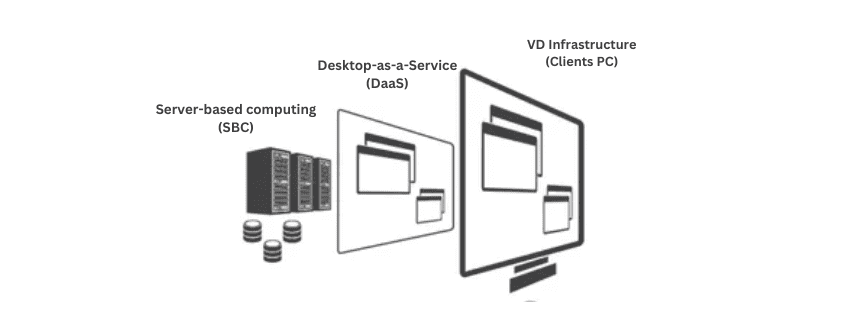
- Server-based computing (SBC): The older model where all virtual desktops are held in one central server farm.
- Desktop-as-a-Service (DaaS): The third party manages and hosts the entire VDI infrastructure. It is a cloud model of VDI.
- VD Infrastructure: It stores the Virtual Desktop Client, also referred to as thin client software, or even sometimes simple PC clients with software.
Highly Recommended: Why Would You Need A Dedicated Server For Accounting Offices ?
Persistent VDI vs. Non Persistent VDI
The choice between the two becomes imperative for a business:
Persistent VDI:
In a persisting VDI, a dedicated and unique virtual desktop is assigned to each user. This desktop is owned by that particular user, and its state, configurations, and installed applications remain intact between sessions. This means that the users get the familiarity and personalization of the computing experience so much like a physical traditional desktop. It’s especially helpful for those users who need a specific workspace with certain software packages and settings consistent from session to session.
Non-Persistent VDI:
In a non-persistent VDI environment, users are assigned to a pool of virtual desktops instead of dedicated virtual desktops. This means that each time a user logs in, the system assigns one of the desktops from the pool. When a session is complete, the VM returns to the pool, overwriting any session-specific changes it may have encountered. This concept is often described as “stateless VDI” because, after each use, the virtual desktops return to their original state.
The choice of persistent and non-persistent VDI depends on many factors, including the needs of users, budget, and available IT resources in an organization. Persistent VDI is recommended for users who have to be personalized and need consistency in their computing experience. Users like designers, developers, and knowledge workers can benefit from it. Non-persistent VDI is better suited for large user bases who just need to do basic computing with less need for personalization.
Key Benefits of VDI
VDI comes with a broad range of advantages for businesses and organizations:
- Increased Security: Data is centralized stored and managed on the server, thus making it easy to implement solid security measures like encryption, access controls, and regular backups. This central control reduces the chances of data breach and theft substantially. Users can access their working environment from any available device, so the risk of data exposure through lost and stolen devices is thus minimized. In case a device is lost or stolen, the IT administrators can wipe out the virtual desktop remotely; in this way, sensitive data will remain safe.
- Increased flexibility and mobility: employees can work anywhere that has an internet connection otherwise there is remote work, telecommuting, and flexible work arrangements; through their devices- laptops, tablets, smartphones- employees can enhance their productivity and satisfaction of the employee. It is an excellent disaster recovery solution for VDI since one can access their work environment from a different location during cases of localized system failure, or any case of a natural disaster.
- Increased Productivity and Efficiency: Desktops, applications, and updates can be centrally managed in an organization to make IT operations smooth, minimize administrative overheads, and thereby free up IT resources for other important work. Deployments and updates of software can be managed easily and rolled out to all users simultaneously. Applications can be centrally deployed and updated without any effort on the applications to have uniform performance and to minimize the occurrences of software conflicts.
- Improved User Experience: Virtual desktops can be set as per individual user requirements so that working becomes better. VDI can render performance in all machines irrespective of their physical hardware. Since remotely, IT support can easily diagnose and troubleshoot problems, this also minimizes downtime and improves user satisfaction.
- Reduced IT Overhead: The underlying infrastructure is taken care of by the cloud provider, which unshackles IT resources for other business-critical tasks.
- Pay-as-you-go Pricing: Typically, the pay-as-you-go model is characteristic of cloud-based VDI; here, the organization pays only for resources consumed.
- Improved Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based VDI is equipped with disaster recovery.
This will ensure that in the event of a crash or a natural disaster of a local system, it shall not disrupt business operations
Importance of VDI Security
A Security Core of the IT Infrastructure and VDI Is No Exception. There are several key considerations for security during implementations of VDI:
- Data Encryption: Ensure the use of proper mechanisms for encryption: At rest and data in transit Strong Authentication-Apply MFA for better authentication of users so that unauthorized users cannot access certain applications, data, and other resources.
- Network security. A firewall and intrusion detection system among others, will be employed to protect the network infrastructure against any sort of unauthorized access.
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing: Performs regular security audits and penetration testing to detect all the probable weaknesses.
The Top VDI Remote Desktop Protocols
Most of the time, VDI uses remote desktop protocols in which users interact with the virtual desktop. The commonly used protocols include:
Remote desktop protocol: RDP is among the most common protocols in use to connect a user to the Windows-based remote desktop.
Virtual Network Computing (VNC): It is a platform-independent protocol, which allows remote desktop access from a variety of operating systems.
Find More : What To Do Next If Sage 50 Cannot Connect To Database Server.
Conclusion
What is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure? One of the revolutionary technologies that change businesses and organizations up to a very large extent is Virtual Desktop Infrastructure. It comes with many advantages: there is decoupling of user experience with a physical device so it increases the level of security, improves the level of flexibility, and augments productivity, but at reduced costs.
Hence, such a demand arises for cloud computing and cloud-based VDI solutions that can easily scale with the organization and, by their deployment, bring some degree of flexibility along with some savings in the costs. If you need professional advice, contact our VDI Engineer at (800) 217-0394 or chat with our live expert through the Chat-box for cloud and hosting services..
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the main differences between on-premises VDI and Cloud-based VDI?
The fundamental differences between on-premises VDI and cloud-based VDI (DaaS) involve the degree of control, cost, scalability, maintenance, and security responsibilities one is expected to handle. For on-premises VDI, your organization owns and runs the entire infrastructure, including the servers, storage, and networking, giving you total control but huge investments in terms of hardware, software, and IT personnel in terms of maintaining and managing these infrastructures. On the contrary, cloud-based VDI provides a third party to manage your entire infrastructure on your behalf, whereby you pay based on a subscription basis. This eradicates the massive upfront investment as well as the burdens of infrastructure management. However, it may somewhat limit your control over certain aspects of the environment.
What is the minimum internet speed needed for a good VDI experience?
The minimum speed requirements of the internet to get a good experience in VDI are determined by various factors, such as the number of users at one time, types of applications being used (such as graphics-intensive applications compared to office productivity applications), and the level of performance desired-for example, “acceptable latency” and video quality.
How does VDI impact device compatibility?
VDI is highly compatible with devices. Virtual desktops can be accessed by users through any device: laptop, desktop, tablet, and smartphone, so long as it has a client application compatible with the device and has an Internet connection. With this, the employees are given the freedom to work anywhere while using the preferred devices for higher productivity and satisfaction
What are the significant security risks for VDI?
VDI has enhanced security in many ways, but some security risks arise because of this. Some significant security issues that have been found are data breaches, unauthorized access, insider threats, malware attacks, and adhering to certain regulations of their industries. To eliminate all these risks and to protect the sensitive data that the organizations keep, they must implement some good security measures: encryption of data, robust authentication, good controls on access, and regular audits for security issues
What are the key considerations when selecting a VDI solution?
Several key factors to consider when deciding on a VDI solution involve the overall budget, which might include capital expenditure and operational expenditures for on-premises versus cloud-based. Scalability ensures that virtual desktops can quickly be increased or decreased based on business needs. Security provided by the company, integration capabilities with existing infrastructure, and levels of technical support are also key aspects to consider.

Brown Lopez is a Cloud Engineer and technical writer based in Austin, USA, who enjoys turning complex cloud ideas into clear, simple insights. With solid experience in cloud architecture and real-world projects, he loves creating practical content that helps professionals understand, build, and improve their cloud solutions with confidence.